No Farmers, No Food, No Life
No Farmers, No Food, No Life
The world is now facing a man-made food catastrophe. It is reaching crisis levels.Current policies in many parts of the world place a priority on climate change for realizing a green new deal. Meanwhile, such policies will contribute to children dying from severe malnutrition due to broken food systems, with shortages of food and water, stress, anxiety, fear , and dangerous chemical exposure.
More negative pressure on farmers and the food system is asking for a catastrophe. The immune system of many people, especially children, has lost its resilience and has weakened too far with high risks for intoxication , infections, non-communicable and infectious diseases, deaths and infertility.
Dutch farmers , of whom many will face a cost of living crisis after 2030, have drawn the line. They are supported by an increasing number of farmers and citizens worldwide.
It’s not the farmers who are the most heavy polluters of the environment, but industries who make the products needed for a technocracy revolution to green energy, data mining, and Artificial Intelligence. As more of the WEF plans are rolled out by politicians, inequalities grow, and conflicts are rising all over the world.
The strong farmers’ revolt in the Netherlands is a call for an urgent transition to a people-oriented, free and healthy world with nutritious food cultivated and harvested in respect to natural processes. The cooperation of ordinary people worldwide is on the rise to prevent a mass famine catastrophe caused by the plan of scientism and technocracy to rule and control the world by unelected scientists and elites.
Enough food, access to food is the problem
Farmers around the world normally grow enough calories (2,800) per person (while 2,100 calories/day would be sufficient) to support a population of nine to ten billion people worldwide. But still over 828 million people have too little to eat each day. The problem is not always food; it is access. The UN which wrote in 2015 in the Sustainable Development Goals goal 2: No hunger and malnutrition for all in 2030 will not be reached.
Throughout history many times natural or manmade disasters led to food insecurities for longer periods of time, resulting in hunger, malnutrition (undernourishment) and mortality. The Covid-19 pandemic has worsened the situation. Since the global pandemic began, access to food estimates show that food insecurity has likely doubled, if not tripled in some places around the world.
Moreover, during the pandemic, global hunger rose to 150 million and is now affecting 828 million people, with 46 million at the brink of starvation facing emergency levels of hunger or worse. In the hardest hit places, this means famine or famine-like conditions. At least 45 million children are suffering from wasting, which is the most visible and severe form of malnutrition, and potentially life-threatening.
With global prices of food and fertilizers already reaching worrying highs, the continuing impacts of the pandemic, the political forces to realize climate change goals and the Russia-Ukraine war raise serious concerns for food security both in the short and the long term.
The world is facing a further spike in food shortages, pushing more families worldwide at risk for severe malnutrition. Those communities which survived former crises are left more vulnerable to a new shock than before and will accumulate the effects, diving into famine (acute starvation and a sharp increase in mortality).
Furthermore, growth of economies and development of nations are currently slowing down due to a lack of workforce due to a sharp decrease in well-being and higher mortality rates.
In the wake of new nitrogen limits that require farmers to radically curb their nitrogen emissions by up to 70 percent in the next eight years, tens of thousands of Dutch farmers have risen in protest against the government.
Farmers will be forced to use less fertilizer and even to reduce the number of their livestock, in some cases up to 95%. For smaller family-owned farms it will be impossible to reach these goals. Many will be forced to shutter, including people whose families have been farming for up to eight generations.
Moreover, a significant decrease and limitations of Dutch farmers will have huge repercussions for the global food supply chain. The Netherlands is the world’s second largest agricultural exporter after the United States. Still, the Dutch government pursues their agenda on Climate Change while there is currently no law to support the implementation, while they will not change much in the planet’s major air pollution. Models used to arrive at the decision of the Dutch government are debated by acknowledged scientists.
In no communication have Dutch politicians considered the effects of their decision on breaking a most important goal in the UN agreement: ending hunger, food insecurity and malnutrition in all in 2030.
Unfortunately, Sri Lanka , a country whose political leader introduced zero Nitrogen and CO2 emissions policy, is now facing economic problems, severe hunger, and difficulties to access food upon a political decision that farmers were not allowed to use fertilizers and pesticides. Still, politicians responsible for Nitrogen emissions/climate change in other countries pursue the same green policy.
Furthermore, experts are warning that heat, flooding, drought, wildfires, and other disasters have been wreaking economic havoc, with worse to come. Food and water shortages have been in the media.
On top of that, Australian experts announce a risk for an outbreak of a viral disease in cattle. This could cause an A$80 billion hit to the Australian economy and even more real supply chain issues. Countless businesses and producers go bankrupt. The emotional toll they are facing to euthanize their healthy herds is immense and hardly bearable. It is pushing more farmers to end their life.
Hopefully, the need for the Danish government to apologize , as an investigative report on the cull of more than 15 million minks in November 2020 criticized the action that led to the misleading of mink breeders and the public and the clearly illegal instructions to authorities, will help politicians to reconsider such drastic measures on farmers.
Worldwide, farmers’ protests are rising, supported by more and more citizens who stand up against the expensive mandates for changes to “green policies” that already brought massive miseries and instability.
At a ministerial conference for food security on June 29 2022, UN Secretary-General Antonio Guterres warned that worsening food shortages could lead to a global “catastrophe ”.
Malnutrition responsible for more ill health than any other cause
The increased risk of food and water shortages the world is facing now will bring humanity to the edge. Hunger is a many-headed monster. For decades conquering world hunger has become a political issue in a way that it could not have been in the past. The use of authoritarian political power led to disastrous government policies, making it impossible for millions of people to earn a living. Chronic hunger and the recurrence of virulent famines must be seen as being morally outrageous and politically unacceptable, says Dreze and Sen in Hunger and Public Action , published in 1991.
“For those at the high end of the social ladder, ending hunger in the world would be a disaster. For those who need availability of cheap labor, hunger is the foundation of their wealth, it is an asset,” wrote Dr. George Kent in 2008 in the essay “ The Benefits of World Hunger.”
Malnutrition is not only influenced by food and water shortage, but also to exposures of extreme stress, fear, insecurity of safety and food, social factors, chemicals, microplastics, toxins, and over-medicalization. No country in the world can afford to overlook this disaster in all its forms, which affects mostly children and women in reproductive age. Globally more than 3 billion people cannot afford healthy diets. And this is in contradiction to what many people think is just a low-income country problem.
Even before the Covid-19 pandemic began, about 8% of the population in North America and Europe lacked regular access to nutritious and sufficient food. A third of reproductive-age women are anemic, while 39% of the world’s adults are overweight or obese. Each year around 20 million babies are born underweight. In 2016 9.6% of the women were underweight. Globally in 2017, 22.2% of the children under the age of five were stunting, while undernutrition explains around 45% of deaths among children under five.
As stated by Lawrence Haddad, the co-chair of the Global Nutrition Report independent Expert Group, “We now live in a world where being malnourished is the new normal. It is a world we must all claim as totally unacceptable.” While malnutrition is the leading driver of disease with nearly 50% of deaths caused by nutrition related non-communicable diseases in 2014, only $50 million of donor funding was given.
Malnutrition in all its forms imposes unacceptably high costs – direct and indirect – on individuals, families and nations. The estimated impact on the global economy of the chronic undernourishment of 800 million people could be as high as $3,5 trillion per year , as was stated in a Global Nutrition Report in 2018. While child deaths, premature adult mortality and malnutrition-related infectious and non-communicable diseases are preventable with the right nutrition.
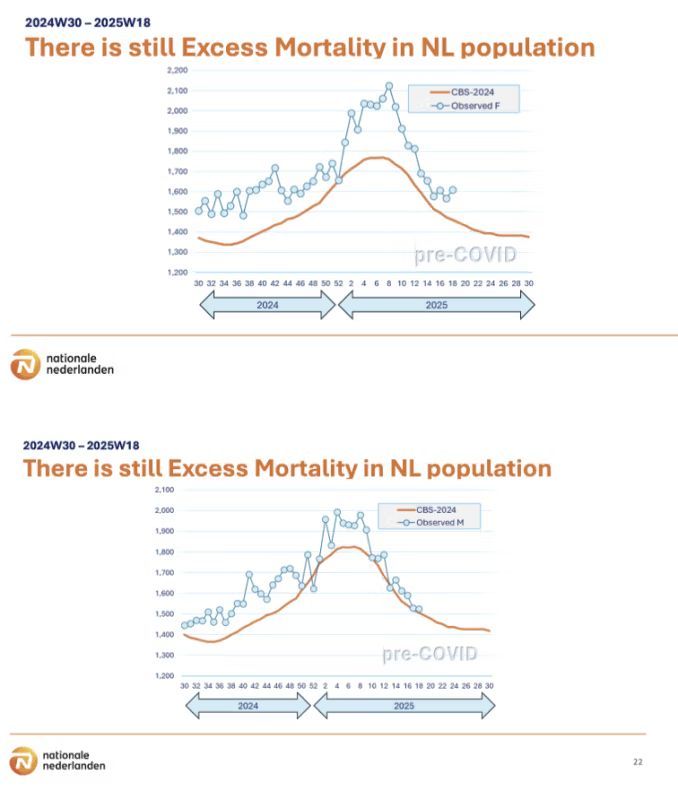
This will be much more at this precious moment, as the population sharply increases in excess mortality and non-communicable diseases among the working age people as recently shown by insurance companies.
Famines cause transgenerational effects
Famine is a widespread condition in which a large percentage of people in a country or region have little or no access to adequate food supplies. Europe and other developed parts of the world have mostly eliminated famine, though widespread famines that killed thousands and millions of people are known from history, like the Dutch Potato famine from 1846-1847, The Dutch Hunger winter 1944-1945 and a Chinese famine of 1959-1961.
The latter was the most severe famine both in terms of duration and number of people affected (600 million and around 30 million deaths) and led to a widespread undernutrition of the Chinese population in the period from 1959-1961. Currently, Sub-Saharan Africa and Yemen are countries with recognized famine.
Unfortunately, global destabilization, starvation and mass migration are increasing fast with more famines to be expected if we do not act today.
Epidemiological studies of Barker and later of Hales showed a relation between the availability of nutrition in various stages of pregnancy and the first years of life and diseases later in life. Their studies demonstrated that people with metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular diseases were often small at birth. More and more research proves the role of nutrition-related mechanisms influencing gene expression. Even the period prior to pregnancy might influence a later risk for insulin resistance or other complications of the fetus.
As demonstrated in a study with 3,000 participants in Northern China, prenatal exposure to famine significantly increased hyperglycemia in adulthood in two consecutive generations. Severity of famine during prenatal development is related to the risk for Type 2 diabetes. These findings are consistent with animal models that have shown the impact of prenatal nutritional status on neuro-endocrine changes that affect metabolism and can be programmed to transmit physiologically across multiple generations through both male and female generations. Early life Health shock conditions can cause epigenetic changes in humans that persist throughout life, affect old age mortality and have multigenerational effects. Depending on which trimester the fetus is exposed to food deprivation or even stress alone a related disease later in life may vary from schizophrenia, ADHD to renal failure and hypertension among others. Other studies of famine exposure in people have produced evidence of changes in the endocrine system and to prenatal gene expression in reproductive systems.
The effects of periods of famine or undernutrition have predominantly been seen in people with low social economic income. However, 1 in 3 persons in the world suffered from some form of malnutrition in 2016. Women and children are 70% of the hungry. There is no doubt that undernutrition increased further during the past six years. Stunting and wasting increased in the most vulnerable. Two out of three children are not fed the minimum diverse diet they need to grow and develop to their full potential.
The hungry people in countries like Sri Lanka, Haiti, Armenia ,and Panama are the tip of the iceberg, opening the eyes of many citizens worldwide to a fast-growing problem as a result of the lockdowns, mandates and coercive policies in climate change, drought and the Ukraine war.
Citizens of the world have been facing for years: excess mortality , a fast decline in infertility and childbirth with a threat to human rights for women and more diseases.
Shocking reports of the UN and WHO acknowledged the health of people and environment is declining. The world is moving backwards on eliminating hunger and malnutrition. The real danger is that these numbers will climb even higher in the months ahead.
The truth is that food innovation hubs , food flats (vertical farming), artificial meats and gene and mind manipulations will not be able to tackle the depressing state humanity is facing.
Zero-Covid policy has brought humanity at risk in its existence. Covid-19 vaccines with a risk for harm have been rolled out even for children under five years, hardly at risk for a severe disease, but undernourishment that greatly increases susceptibility to major human infectious diseases has not been taken care of.
Conflicts are growing worldwide, increasing instability. Citizens will no longer accept policies without a clear harm-cost benefit analysis.
We need to act now to decrease food and fuel prices immediately by supporting farmers and effective food systems for nutritious food to heal the most malnourished (children and females at childbearing age) in the population.
Let us hope for a return of Hippocrates’ principle: “Let food be thy medicine and medicine be thy food.”
Het bericht No Farmers, No Food, No Life verscheen eerst op Good Care Feels Better.